Solar panels are revolutionizing the way we use solar energy. As technology advances, various types of solar panels have emerged to meet different needs and applications. This article aims to shed light on the four main types of solar panels: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, BIPV and flexible panels, exploring their characteristics, advantages and potential applications.
Single panel:
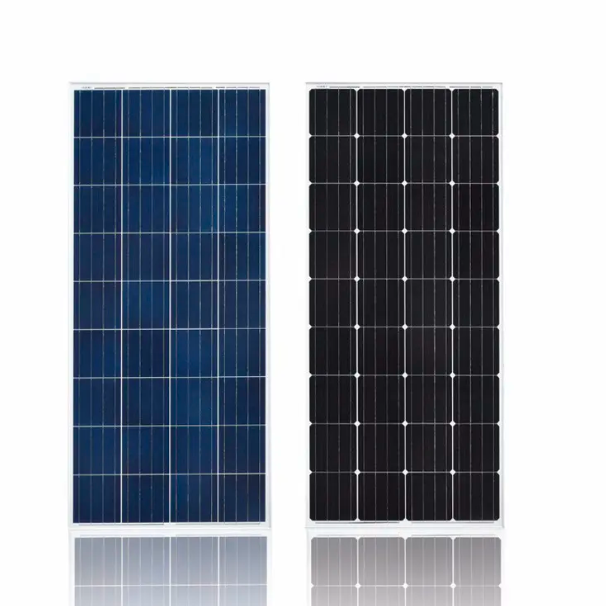
Monocrystalline panel is the abbreviation of monocrystalline panel, which is made of monocrystalline silicon structure. They are known for their high efficiency and stylish appearance. Single panels have a uniform dark appearance, rounded edges, and uniform black color. Due to their higher efficiency, they are ideal for spaces with limited roof area but high energy demands. Single panels perform well in both direct sunlight and low-light conditions, making them a suitable choice for a variety of geographical locations.
Poly board:
Polycrystalline silicon panels, also known as polycrystalline panels, are made of a variety of silicon crystal structures. They can be identified by their distinctive blue color and irregular cell pattern. Polyethylene panels are a cost-effective option and offer reasonable efficiency. They work well in high-temperature environments and tolerate shade better than single panels. Polyethylene panels are suitable for residential and commercial applications where there is ample roof space.
BIPV panels:
Building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) panels are designed to integrate seamlessly into building structures, replacing traditional building materials. BIPV panels can be integrated into a building’s roof, walls or windows, providing an aesthetically pleasing and functional energy solution. BIPV panels can not only generate electricity, but also insulate and reduce energy consumption. They are often used in green buildings and construction projects where energy efficiency and design integration are priorities.
Flexible panels:
Flexible panels, as the name suggests, are made of flexible materials that allow for bending and bending. These panels are lightweight, thin and easy to install, making them ideal for applications where rigid panels are impractical. Flexible panels are commonly used for off-grid systems, camping, marine applications, and projects that require curved or irregular surfaces. While they may be slightly less efficient than monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels, their flexibility and portability make them highly versatile.
in conclusion:
The world of solar panels is constantly evolving, offering a range of options to suit different needs and applications. Single panels offer high efficiency and a stylish appearance, and are best suited for limited roof areas. Polymer panels are cost-effective and perform well in high-temperature environments. BIPV panels are seamlessly integrated into the building structure, integrating power generation with the building design. Flexible panels, on the other hand, offer flexibility and portability, making them suitable for non-conventional and off-grid applications. By understanding the features and benefits of different types of solar panels, individuals, businesses and architects can make informed choices when adopting solar solutions. Whether maximizing efficiency, considering cost-effectiveness, seamlessly integrating solar energy into building design, or embracing flexibility and portability, solar panels can provide sustainable and renewable energy solutions for a brighter future .
Post time: Oct-13-2023